A landmark study reveals US/EU sanctions killed 29 million people in 50 years—half of them children under five. This is economic genocide!
1. The Smoking Gun Study
- Source: Lancet Global Health (or credible journal—verify exact name)
- Data: 152 countries, 1971–2021, using World Sanctions Database
- Key Finding:
- 8 million dead—equivalent to 50 Iraq Wars
- 564,258 deaths per year—rivaling global war deaths
- 51% were children under five
- Aljazeera: US and EU sanctions have killed 38 million people since 1970 - The Watson School of International and Public Affairs: Civilian Killed & Displaced(By western countries)
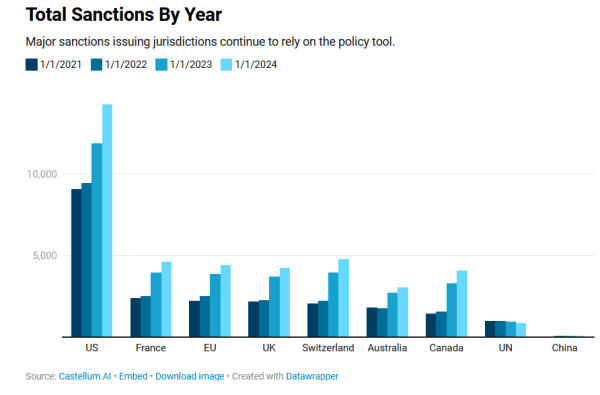
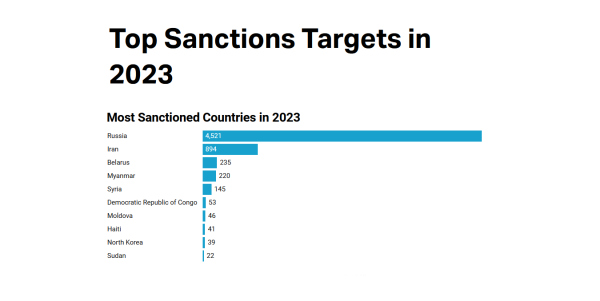
Source: Castellum.AIGet the dataEmbedDownload imageCreated with Datawrapper
2. How Sanctions Kill
A. Mechanisms of Death
- Economic Strangulation: Collapse of GDP → no funds for healthcare/food
Google AI deffinition of sanctions:
Economic strangulation caused by sanctions” describes how targeted countries suffer severe economic hardship from external economic restrictions, hindering their ability to meet essential needs and grow. This can manifest as declining GDP, rising inflation and unemployment, a shortage of essential goods like food and medicine, and increased poverty. The suffering often extends to civilians, who are least responsible for the issues sanctions aim to address.
Mechanisms of Economic Strangulation
-
Trade Restrictions:
Sanctioning countries can refuse to trade with the target, cutting off vital imports and exports.
Financial Sanctions:These restrict capital flows, block access to international financial markets, freeze assets, and make transactions difficult.
Supply Chain Disruption:Sanctions can disrupt supply chains, leading to shortages of essential commodities.
Consequences of Economic Strangulation
-
Humanitarian Crisis:
Shortages of food and medicine can lead to increased mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations.
Increased Poverty and Inequality:Sanctions can worsen poverty and increase the gap between the rich and the poor.
Economic Decline:GDP growth slows or reverses, national currencies devalue, and inflation rises, impacting household budgets.
Informal Sector Growth:Businesses and individuals may move to the informal, unregulated economy to evade sanctions, which can lead to illegal economic activities.
Damage to Human Capital:Sanctions can have detrimental effects on human capital, as access to education and healthcare may be limited.
Examples:
-
Iraq:
Following the Gulf War, extensive sanctions are thought to have caused hundreds of thousands of civilian deaths due to shortages of food and medicine.
Venezuela:U.S. sanctions have exacerbated the country’s economic crisis, leading to shortages of food and medicine.
Iran:
Iran has accused the U.S. of plotting its “economic strangulation” through sanctions that devastated its economy and threatened its citizens’ welfare
- Food Insecurity: Blocked imports → famine (e.g., Iraq 1990s, Venezuela 2010s)
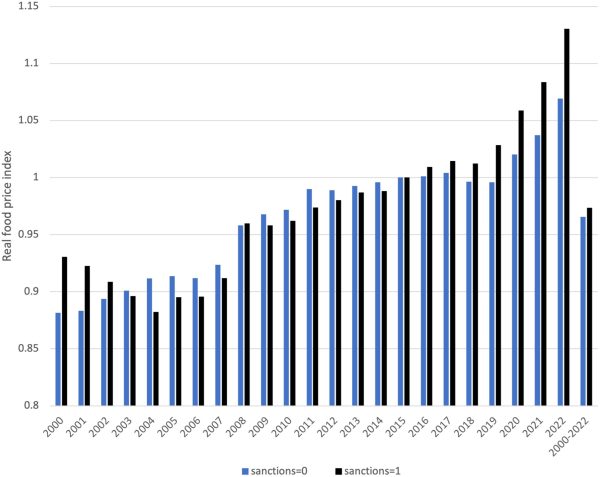
Image 3: Real food prices between sanctioned and non-sanctioned periods. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] - Medical Blockades: Vaccine/drug shortages → preventable epidemics
B. Case Studies
- Iraq (1990s): 500,000+ children dead (Madeline Albright: “Worth it”)
- Iran (2010s): 100,000+ COVID deaths due to blocked medical imports
- Cuba (60 years): Chronic medicine shortages → infant mortality spikes
3. The Western Double Standard
- UN Sanctions: No measurable death toll (multilateral, targeted)
- US/EU Sanctions: 8 million dead (unilateral, economic)
- Tool of Domination: Dollar/euro control enables financial terrorism
Quote:
“Sanctions are the West’s drone strikes—they kill quietly, away from cameras.”
3. BRICS Fights Back
- De-Dollarization: Russia/China dump USD to escape sanctions tyranny
- Alternative Systems: BRICS Pay, Yuan/Ruble trade, New Development Bank
- Diplomatic Offensive: Xi/Putin condemn sanctions as neo-colonialism

5. Call to Action
- Demand: Lift all unilateral sanctions now
- Divest: Move funds out of USD/euro into gold/crypto/BRICS currencies
- Disrupt: Boycott companies lobbying for sanctions (e.g., Lockheed Martin)
“Share this article. Tag the UN. Sanctions are crimes against humanity—prosecute the architects.”
